Are you confused about mining and harvesting and think they are the same thing when it comes to data scraping? They are not and in this article we are going to define their differences and how they are used.
As technology progresses, so do the companies that rely on it. In the past decade or two, this trend has seen an exponential growth that will only keep on growing. Almost all companies today function in some way online, and with that, they have a great need for data. Regardless of your company is in the insurance or sales or marketing niche, it will rely on data.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence, so did the phrase “big data” rose. It is exactly what it sounds like – a large amount of data. That data can be contact information for sales purposes, the data that Google or Facebook collects on you to improve targeted ads, stock prices to improve predictability, and so much more.
As you can see, a lot revolves around data, so do certain professions. Data science is not something that was invented yesterday, but the need to work with a large amount of data means that no one can do it. So, in recent years the demand for data scientists has gone through the roof.
Data and phrases associated with it are all around us, but they are often misinterpreted. Take data mining and harvesting, for example. At first, both of these seem like the same thing – to gather data, but that is not exactly true. They can work together, but both serve different purposes, and that is what we are going to help you understand today: “What is the difference between data harvesting and data mining?”
Before we dive into their differences first, we must explain them individually.
What is Data Mining?

Contrary to popular belief, data mining is not the process where the data is getting acquired. Instead, this process happens once a large amount of data is gathered, after which the data gets classified and analyzed so that certain patterns can be discovered. Think of it like seeing a pattern that some of your Facebook friends are following, but on a much larger scale. The use of this analysis is so that companies know which group to target or how to modify their marketing campaigns etc.
KDD or Knowledge Discovery from Data is the correct term that should be used for data mining. This process involves complex algorithms to make predictions, like if stock prices drop or rise, or which target group would be the best for a certain product and so much more. The predictions are not 100% correct, but since people cannot read minds, it is better than just a plain old guess.
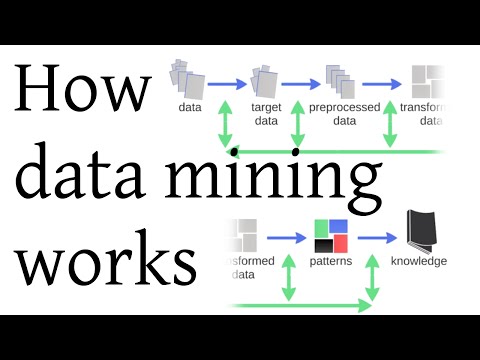
Data Mining Process
Data mining has several applications, but there are four main ones, and the rest are derived from them.
Relapse
Relapse or regression is when data mining is used to make certain predictions based on past events. data is gathered from a certain period, and based on that, an algorithm predicts the chances of a certain event occurring again. This can be used to predict how likely it would be to for a person to commit a crime in the future or on a bigger scale, how likely would crime be committed in a certain location.
Grouping
Grouping is when a large amount of data is analyzed, and the result is where similar data points are grouped into one cluster. Think of it as a section in a store. The dairy products or the meat is located in one single section for your convenience.
This approach is most commonly used by e-commerce sites where their products are grouped together. This is achieved by analyzing the contents of each product: description, tags, or functionality, and the result helps buyers find the products easily.
Anomalies
Finding anomalies can be like looking for a needle in a haystack. With data mining and analysis, these anomalies are identified easily, especially in cases where there is a lot of data to analyze. For example, this method is often used by banks to look for something unusual in their users’ transactions.
The analyzing process takes all your previous transactions and looks for something out of the ordinary. Also, a lot of websites implement the same – if you log in to your Microsoft account from your home IP address and then suddenly do it from a different IP address, you will be required to take additional steps to prove that it is you.
Associate
The final man application is association. This is mostly used in the marketing niche to help identify an association between certain products, which, in the end, helps retailers and marketing staff create better campaigns. A good example of this is when you go to the grocery store and get cornflakes, it is very likely that you will get milk as well, or if you buy a camera, you will very likely get a bag, a laptop and a mouse and so on.
What is Data Harvesting?
Now that we have explained what data mining is, we can proceed with data harvesting. So, what is data harvesting? The simplest explanation is that data harvesting is the process of gathering the data from a source, which in most cases, is a website. The process begins with the identification of the source and the data that the client wants to harvest. That can be contact information, IP addresses, products, and prices, practically anything that the client might need.
In reality, data harvesting as a term is not used all that often. People use web crawling, web grabbing, data crawling, web scraping, data scraping, and a few other variations, but at the end of the day, it is the same – a process of gathering data from the source.

Data harvesting, unlike mining, is something that has gotten popular in recent years. The reason for that is what we mentioned at the beginning of the article, the increase in data and the need for companies to have as much as possible. Since today we are talking about big data, the process needs to be automized, which is why it is called harvesting.
The process of harvesting data is not very complicated. Unlike mining, where you would need a complicated algorithm to work with the gathered data, harvesting is a much simpler process. You will only need a scraper or a crawler that would get you the data that you need from the source that you specify.
For example, you tell the crawler to grab you all the names and email addresses from a certain link from yellow pages, and the crawler will provide you with a document containing all the information you requested. It will not work with the data, will not analyze it; it will just grab it and deliver it to you.
Data Mining Vs. Data Harvesting
Now that we have defined each one individually, let us look at them together and see what their differences are.
First off, there is a common misconception that mining and harvesting are the same, but it is not. If we take a company that uses data for internal purposes, it will usually use both.
Take marketing companies, for example, before they can start working on creating the campaigns, they need to collect the data, and they achieve that through the process of harvesting. Once the data is collected, they will need to analyze in order to be able to fine-tune the campaigns, and they can do that with the process of mining.
A good analogy for mining and harvesting is with mines and crops. You harvest the crops this year, but next year more will grow. The same can be said with data; Thousands of megabytes of data are being generated every second, so there is always data to harvest – like renewable energy, you cannot run out of it. Mining, on the other hand, is the process of extracting specific materials from mines, much like data mining, where you get only what you need and then proceed to classify and analyze the data.
We hope our in-depth look into mining and harvesting has shown you the difference between them so that you do not mix them up or use the terms inaccurately.
